
The IB Primary Years Programme (PYP) for children aged 3 to 12 nurtures and develops young students as caring, active participants in a lifelong journey of learning.
国际文凭小学课程:培养学生成长为积极的终身学习者
The PYP offers an inquiry-based, transdisciplinary curriculum framework that builds conceptual understanding. It reflects the best of educational research, thought leadership and experience derived from IB World Schools. The PYP has evolved to become a world leader in future-focused education.The PYP is an example of best educational practice globally, responding to the challenges and opportunities facing young students in our rapidly changing world.
国际文凭小学课程提供了一个以探究为基础的跨学科课程框架,以培养对概念的理解。它反映了国际文凭世界学校的最佳教育研究、思想领导力和经验。国际文凭小学课程计划在以未来为重点的教育方面,PYP 已发展成世界领先的教育机构。国际文凭小学课程是全球最佳教育实践的典范,能够应对年轻学生在瞬息万变的世界中所面临的挑战和机遇。
What is the IB Primary Years Programme (PYP)?
什么是国际文凭小学课程(IBPYP)?
The PYP curriculum is a student-centered approach to education for children aged 3-12. The framework begins with the premise that students are agents of their own learning and partners in the learning process. It prioritizes people and their relationships to build a strong learning community.
国际文凭小学课程是针对年龄3-12岁的学生设计的。它注重在课堂内外将儿童培养成为全面发展的探究者。国际文凭小学课程是一个教学体系框架,该框架的前提是,学生是自己学习的主体,是学习过程中的伙伴。它优先考虑人与人之间的关系,以建立一个强大的学习社区。
PYP students use their initiative to take responsibility and ownership of their learning. By learning through inquiry and reflecting on their own learning, PYP students develop knowledge, conceptual understandings, skills and the attributes of the IB learner profile to make a difference in their own lives, their communities and beyond.
国际文凭小学项目学生发挥主观能动性,承担起学习的责任和自主权。通过探究学习和对自己的学习进行反思,PYP 项目的学生发展了知识、概念理解、技能和国际文凭学习者的特质,从而在自己的生活、社区和其他方面有所作为。
The framework emphasizes the central principle of agency, which underpins the three pillars of school life:
• the learner
• learning and teaching
• the learning community
该框架强调 “代理 “这一核心原则,它是学校生活的三大支柱:
·学习者
·学习和教学
·学习社区
The IB learner profile in the PYP
学生培养目标
• Inquirers 探究者
• Knowledgeable 知识渊博
• Thinkers 勤于思考
• Communicators 善于交流
• Principled 坚持原则
• Open-Minded 胸襟开阔
• Caring 懂得关爱
• Risk-Takers 勇于尝试
• Balanced 全面发展
• Reflective 及时反思




The IB learner profile represents a broad range of human dispositions, capacities and traits that encompass intellectual, personal, emotional and social growth. Developing and demonstrating the attributes of the learner profile is an expression of what the IB means by international-mindedness.
国际文凭学习者培养目标代表了人类广泛的性格特征、能力和特质,涵盖智力、个人、情感和社会成长。发展和展示学习者的特质国际文凭学习者培养目标体现了国际文凭组织的国际视野。国际文凭学习者培养目标贯穿于PYP项目学校生活的方方面面。
The IB learner profile permeates all facets of school life in the PYP. All members of the learning community from the youngest learners to school leaders to parents, educators and beyond, have a responsibility to be guided by and demonstrate a commitment to the development of the IB learner profile attributes.
学习社区的所有成员,从最年幼的学生到学校领导,再到家长、教育工作者和其他人员,都有责任以下列原则为指导,并表现出对发展国际文凭学习者培养目标的承诺所有学习社区成员,从最年幼的学生到学校领导、家长和教育工作者,都有责任以属性。
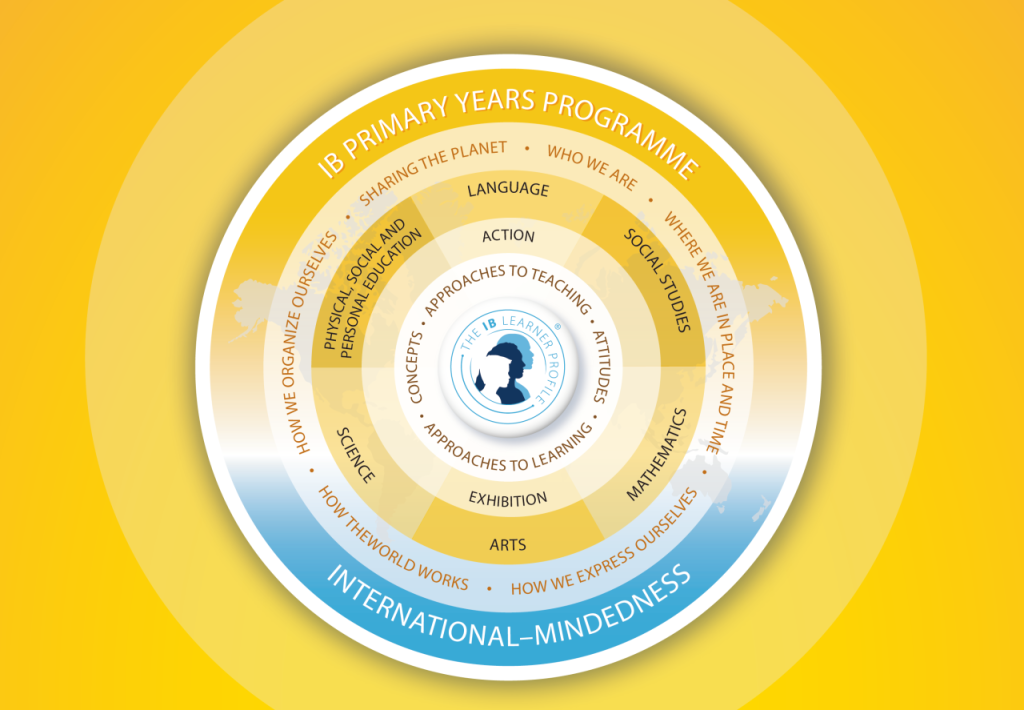
The six subject areas identified within the PYP are
国际文凭小学项目中所明确的6个学科领域是
• language 语言
• social studies 社会学
• mathematics 数学
• arts 艺术
• science 科学
• personal, social and physical education 个人教育、社交教育和体育
Informed by the values described in the learner profile, an IB education
根据国际文凭学习者培养目标中所描述的价值观,国际文凭教育
– focuses on learners—the IB’s student-centred programmes promote healthy relationships, ethical responsibility and personal challenge.关注的焦点是学习者——以学生为中心的国际文凭项目提倡各种健康有益的关系、伦理方面的责任和个人挑战。
– develops effective approaches to learning and teaching—IB programmes help students to develop the knowledge, dispositions and skills needed for both academic and personal success.发展各种有效的教学方法和学习方法——国际文凭项目帮助学生发展他们所需要的各种态度和技能,从而能够在学业和个人成长方面取得成功。
– works within global contexts—IB programmes increase understanding of languages and cultures, and explore globally significant ideas and issues.在全球背景下开展教育——国际文凭项目提高对语言和文化的理解,对具有全球重要性的思想观点和问题进行探索。
– explores significant content—IB programmes offer a curriculum that is broad and balanced, conceptual and connected.探索有重要意义的内容——国际文凭项目提供的课程广泛而平衡,强调对概念的理解和学科之间的联系
The PYP is designed to focus on the development of the whole child as an inquirer, both in the classroom and in the world outside. It is a framework guided by six transdisciplinary themes of global significance, explored using knowledge and skills derived from six subject areas, as well as approaches to learning (ATL) skills. The PYP is flexible enough to accommodate the demands of most national or local curriculums and provides the best preparation for students to engage in the IB Middle Years Programme (MYP).
国际文凭小学项目注重在课堂内外将儿童培养成为全面发展的探究者。小学项目是一个教学体系框架,以具有全球重要性的6个超学科主题为主导,运用在6个学科领域中习得的知识和技能以及超学科技能对它们开展探索,重点强调探究。小学项目具有充分的灵活性来适应绝大多数国家或地方对课程的要求,并使学生为将来学习国际文凭中学项目做好最充分的准备。
The IB Primary Years Programme
国际文凭小学课程
– acknowledges learner agency and the importance of self-ecacy to enable students to become partners in the learning process.
教育学生在知识、社交和情感等方面健康成长。
– addresses students’ academic, social and emotional well-being.
关注学生的学业、社交和情感健康。
– encourages students to develop independence and to take responsibility for their own learning.
鼓励学生养成独立自主性,并对自己的学习负起责任。
– supports students’ efforts to gain understanding of the world and to function comfortably within it.
支持学生努力了解世界,并能够健康快乐地生活其中。
– helps students establish personal values as a foundation upon which international mindedness will develop and flourish.
帮助学生建立起个人价值观,并以此为基础发展和发扬国际情怀
– provides the opportunity to learn more than one language from the age of seven.
提供从七岁起学习一种以上语言的机会。
The PYP is organized around the six transdisciplinary themes. Transdisciplinary learning in the PYP conveys learning that has relevance between, across and beyond subjects and transcends borders connecting to what is real in the world.
国际文凭小学项目围绕六个跨学科主题展开。国际文凭小学项目的跨学科学习是指学科之间、跨学科和学科之外的学习,它超越了国界,与世界上真实的事物相联系。
Through the six transdisciplinary themes, PYP students learn to appreciate knowledge, conceptual understandings, skills and personal attributes as a connected whole. They can reflect on the significance of their learning to take meaningful action in their community and beyond. Through this process of learning in the PYP, students become competent learners, self-driven to have the cognitive, affective and social tools to engage in lifelong learning.
通过六个跨学科主题,国际文凭小学项目的学生学会将知识、概念理解、技能和个人特质作为一个相互联系的整体来理解。他们可以反思学习的意义,在社区内外采取有意义的行动。通过这一学习过程,学生将成为有能力的学习者,自我驱动,掌握终身学习所需的认知、情感和社会工具。




1.Who we are 我们是谁
Inquiry into the nature of the self; beliefs and values; person, physical, mental, social and spiritual health; human relationships including families, friends, communities and cultures; rights and responsibilities; what it means to be human.
对自我本质的探究,对信仰与价值观的探究,对个人、身体、心智、社交和精神健康的探究,对各种人际关系,包括家庭、朋友、社区和文化的探究,对权利与责任的探究对作为人的意义的探究。
2.Where we are in place and time 我们身处什么时空
Inquiry into orientation in place and time; personal histories; homes and journeys; the discoveries, explorations and migrations of humankind; the relationship between and the interconnectedness of individuals and civilizations, from local and global perspectives.
探究的是我们在时空中的方位,个人的历史,家庭和旅程人类的各种发现、探索与迁徙;从本地与全球的观点考察个人与文明之间千丝万缕的联系。
3.How we express ourselves 我们如何表达自己
Inquiry into the ways in which we discover and express ideas, feelings, nature, culture, beliefs and values; the ways in which we reflect on, extend and enjoy our creativity; our appreciation of the aesthetic.
探究的是我们在时空中的方位,个人的历史,家庭和旅程探究我们发现和表达观点、情感、大自然、文化、信仰与价值观的方式,我们反思、扩展、享受我们创造力的方式我们的审美鉴赏。
4.How the world works 世界如何运作
Inquiry into the natural world and its laws, the interaction between the natural world (physical and biological) and human societies; how humans use their understanding of scientific principles; the impact of scientific and technological advances on society and on the environment.
探究自然界以及自然规律;(物质的与生物的)自然与人类社会的互动;人类如何利用他们对科学原理的理解;科技进步对社会与环境的影响。
5.How we organize ourselves 我们如何组织自己
Inquiry into the interconnectedness of human-made systems and communities; the structure and functionof organizations; societal decision-making; economic activities and their impact on humankind and the environment.
探究人类创造的制度与社区之间的相互联系;各种组织的结构与功能;社会决策机制;经济活动及其对人类与环境的影响。
6.Sharing the planet 共享地球
Inquiry into rights and responsibilities in the struggle to share finite resources with other people and other living things; communities and the relationship within and between them; access to equal opportunities; peace and conflict resolution.
探究努力与他人及其他生物分享有限资源时的权利与责任群体以及他们内部及之间的关系;机会均等;和平与解决冲突。
Each theme is addressed each year by all students. (Students aged 3 to 6 engage with four of the themes each year.) These transdisciplinary themes help teachers to develop a programme of inquiries–investigations into important ideas, identified by the schools, and requiring a high level of involvement on the part of the students.
所有学生每年都要学习每个主题(3 至 6 岁的学生每年学习四个主题)。(这些跨学科主题有助于教师制定探究计划–对学校确定的、需要学生高度参与的重要思想进行探究。
Since these ideas relate to the world beyond the school, students see their relevance and connect with it in an engaging and challenging way.
由于这些想法与学校以外的世界有关,学生们看到了它们的相关性,并以一种参与性和挑战性的方式与之联系起来。
Students who learn in this way understand their roles and responsibilities in the learning process. PYP students know that a unit of inquiry involves in-depth exploration of an important idea. They partner with teachers to document and collect evidence of how well they understand that idea.
以这种方式学习的学生了解自己在学习过程中的角色和责任。国际文凭小学项目的学生知道,一个探究单元包括对一个重要观点的深入探究。他们与教师合作,记录和收集他们对这一观点理解程度的证据。
They will expect to be able to work in a variety of ways, on their own and in groups, to allow them to learn to their best advantage.
他们希望能够以各种方式,包括独立学习和小组合作学习来充分发挥自己的学习优势。
EXAMPLE UNIT
Theme: How We Express Ourselves
单元探究例子
主题:我们如何表达自己
1.Central Idea 中心思想
Exploring and expressing ideas, feelings, nature, culture, beliefs, and values through creative activities and aesthetic appreciation enhances our understanding of the world.
通过创造性活动和审美鉴赏来探索和表达思想、情感、自然、文化、信仰和价值观,可以增进我们对世界的了解。
2.Lines of Inquiry 探究方向
Investigate how different art forms can convey ideas, feelings, and cultural values.
研究不同的艺术形式如何传递思想、情感和文化价值观。
Explore how culture influences creative expression and how creative works reflect cultural identities.
探索文化如何影响创意表达,以及创意作品如何反映文化特性。
Develop an understanding of aesthetic appreciation by examining different perspectives on beauty, creativity, and artistic value.
通过研究关于美、创造力和艺术价值的不同观点,培养审美鉴赏能力。
3.Learner Profile and Key Concepts 学习者培养目标以及主要概念
Form, Connection, and Perspective形式、联系和视角
Inquirers, Communicators, Open-Minded勤于探究,善于沟通,思维开放




The Exhibition
学习成果展
In the final year of the PYP, students take part in the PYP exhibition. The exhibition is an authentic process for students to explore, document and share their understanding of an issue or opportunity of personal significance. The whole learning community shares and celebrates this culminating event in the journey students have experienced through their PYP years.
对所有学生来说,学习成果展都是小学项目的一个重要组成部分。在项目的最后一个学年当中,学生们要合作完成一个超学科探究过程,在此过程中,他们要识别实际生活中的难题或问题,对它们开展调查研究并提出解决问题的方法。作为小学项目的结业体验,学习成果展提供了令学生兴奋的机会,让他们展示独立开展工作的能力,并对自己的学习承担责任。


